It's been a while since we released a new mayor version of the jBPM project, but I'm happy to announce that jBPM 7.0.0.Final is now available.
For those not yet familiar with our project, jBPM is a completely open-source Business Process Management (BPM) and case management solution. It supports to full life cycle of processes and cases, from authoring tools through execution all the way to monitoring and management.
For the readers that don't have too much time to read all of the details below, some of the major new features include:
- Case management capabilities
- New simplified authoring experience for creating projects
- Business dashboards
- Process and task admin api
- Process and task console can connect to any (set of) execution server(s)
- Preview of a new process designer and form modeler
- A new security management UI
- Upgrades to Java8, WildFly 10, EAP 7, etc.
A quick introduction to some of the most important features is available below.
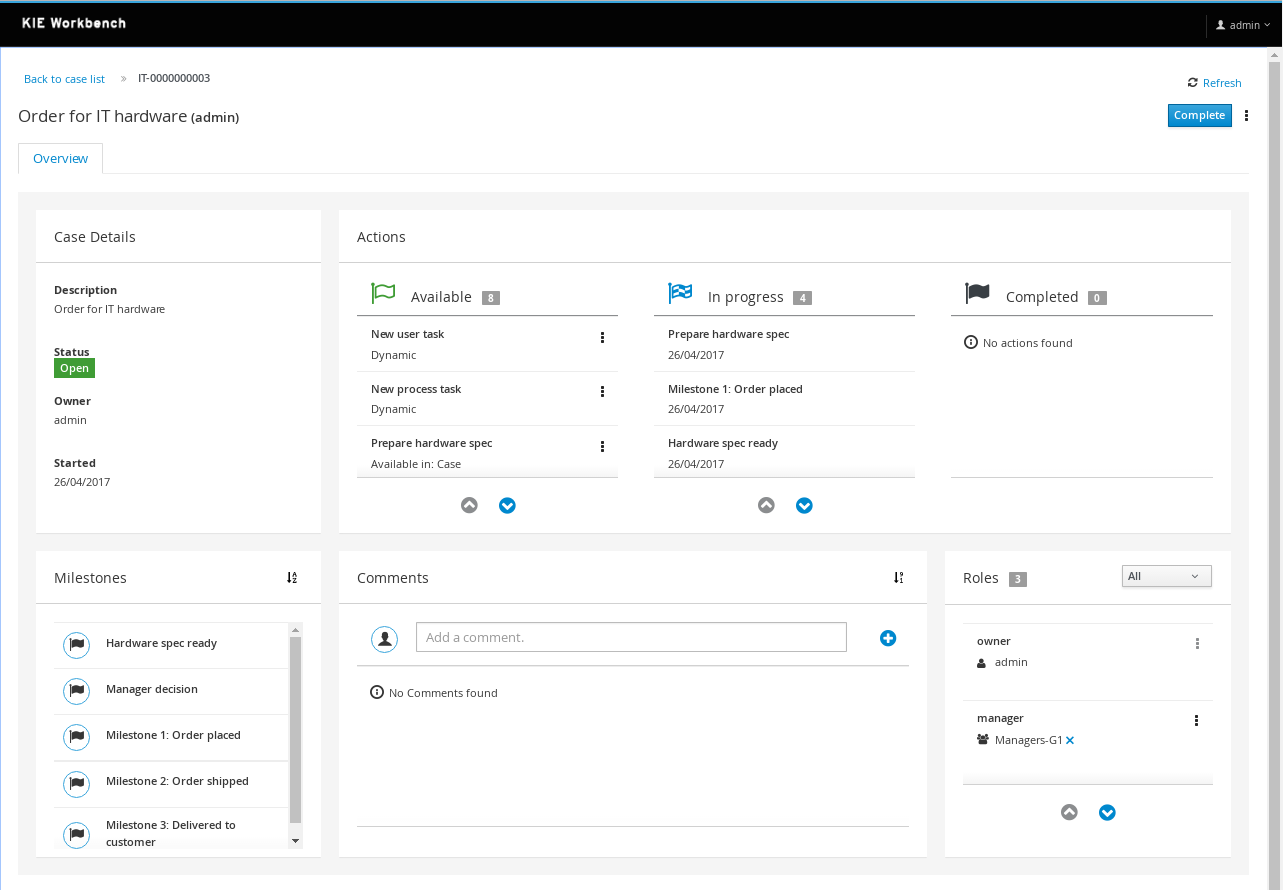
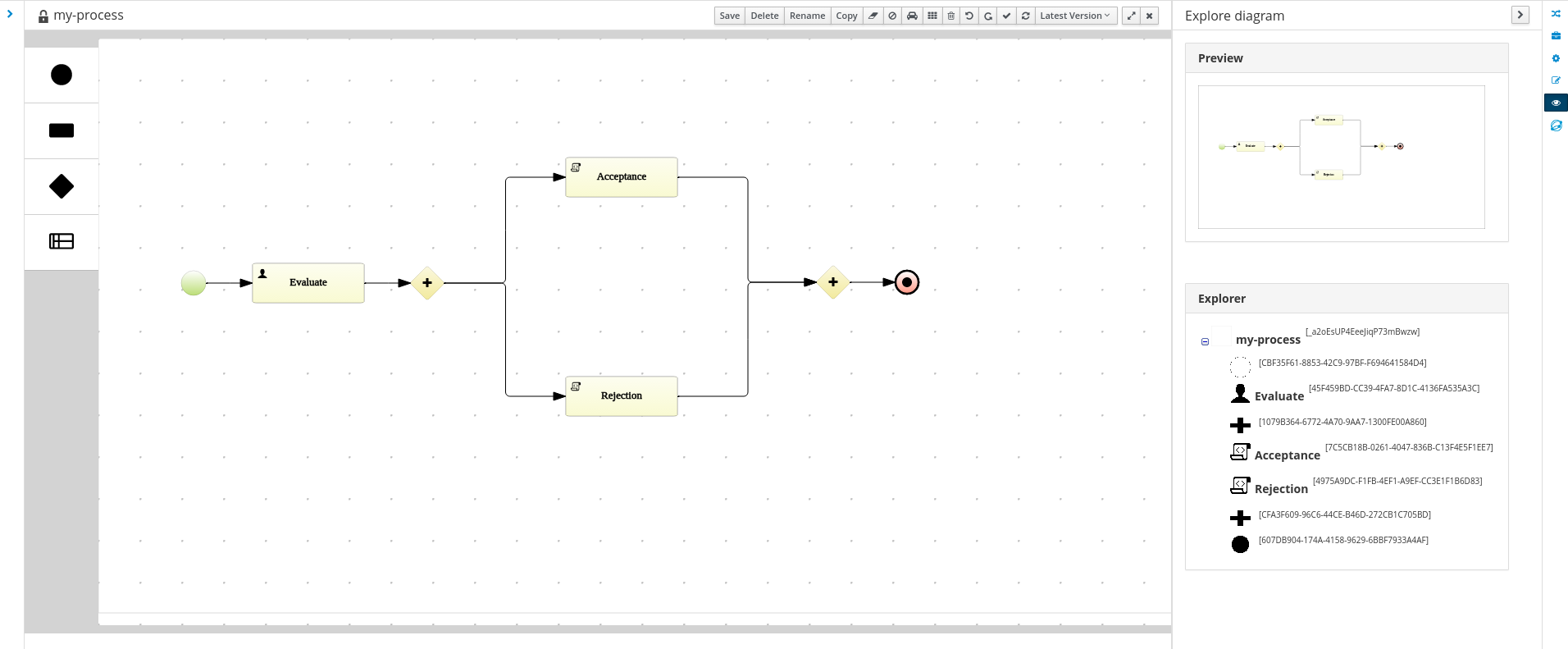
Case management
Case management has been a hot topic in the BPM world for a few years now (and maybe even longer under terms like flexible and adaptive processes etc.). Case management use cases are different from more traditional business processes
since they (typically) require more flexibility and support more
unstructured and unplanned work. Rather than following a nicely
predefined plan from start to finish, actions are more ad-hoc decisions,
what to do next is more based on the data associated with the case, the
end user needs to be given the flexibility to decide what to do next
(although recommendations are welcome), etc.
Ever since v5 our core engine has always had a lot of advanced features to support more flexible and adaptive use cases. While we did introduce some case management building blocks in v6 already, v7 comes with a lot more extensive support for case management use cases:
- Core engine: extended to support more advanced features like case file, ad hoc and dynamic work, stages and milestones, case roles, etc. All these features are available through the remote API as well.
- The web-based authoring environment has been extended to support defining your own cases, with a case project wizard, additional case building blocks and properties in the process editor, etc.
- A new web-based case management UI that showcases how you can use the latest features and manage cases. This UI is built from a number of independent UI building blocks that you can use in your own application as well.
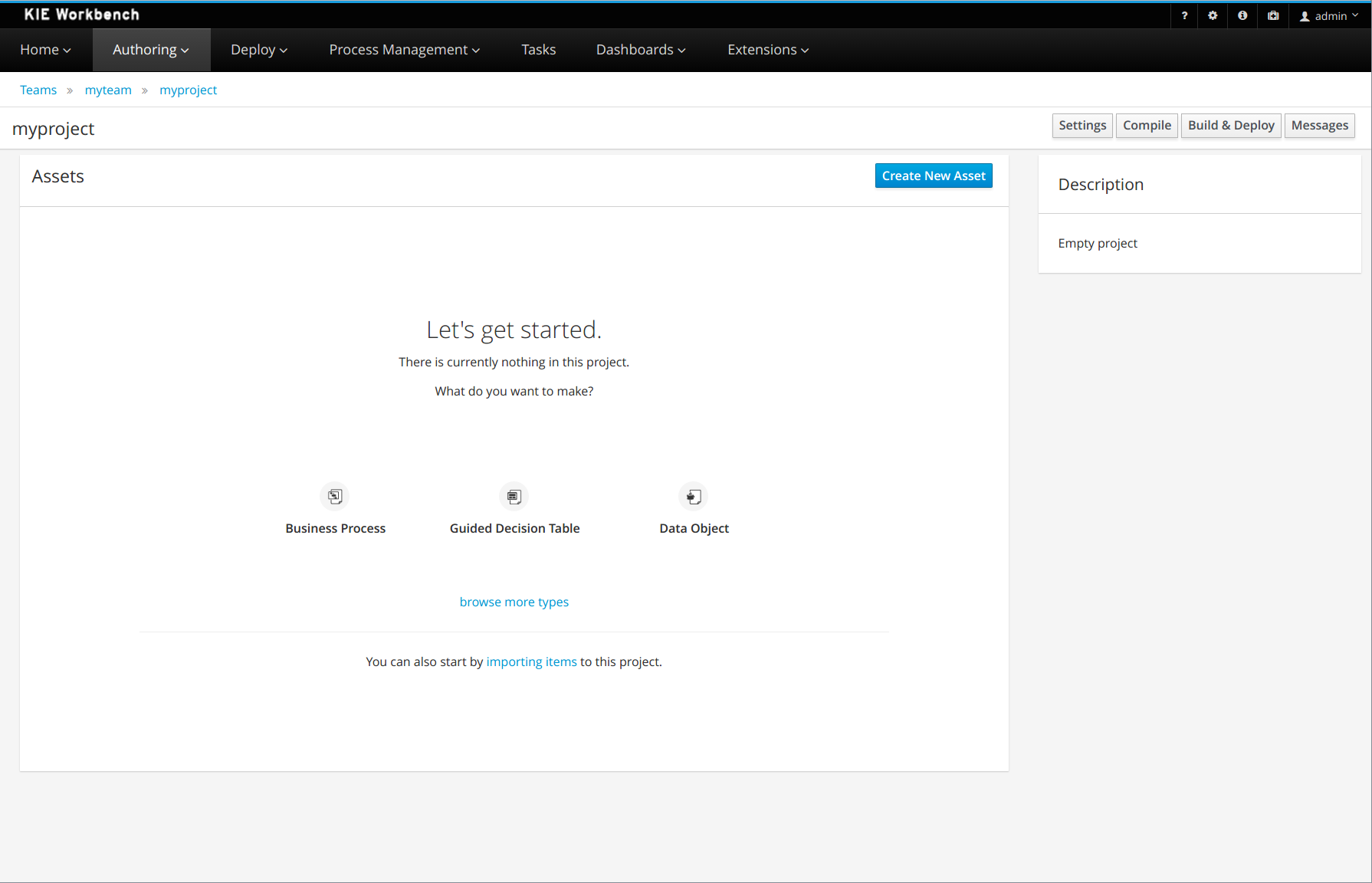
New authoring experience
The experience you get when you open the workbench for the first time, create a new project (or import an example one) and create your first processes, data models and forms has been updated significantly.
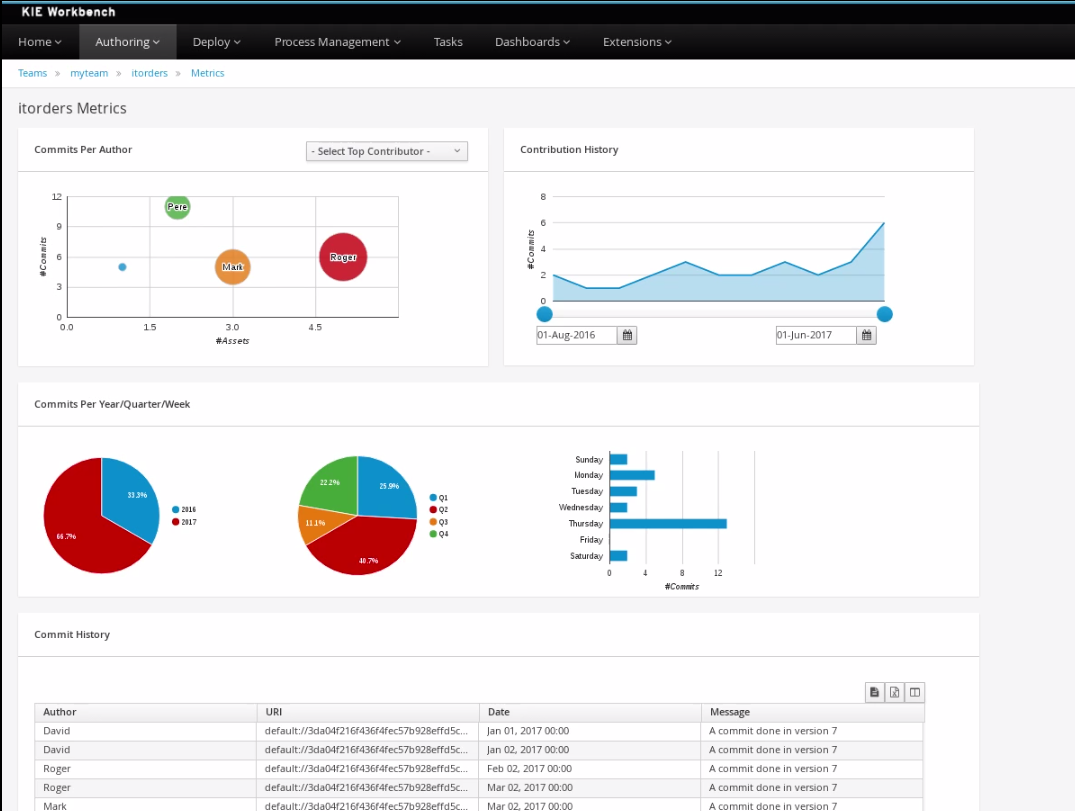
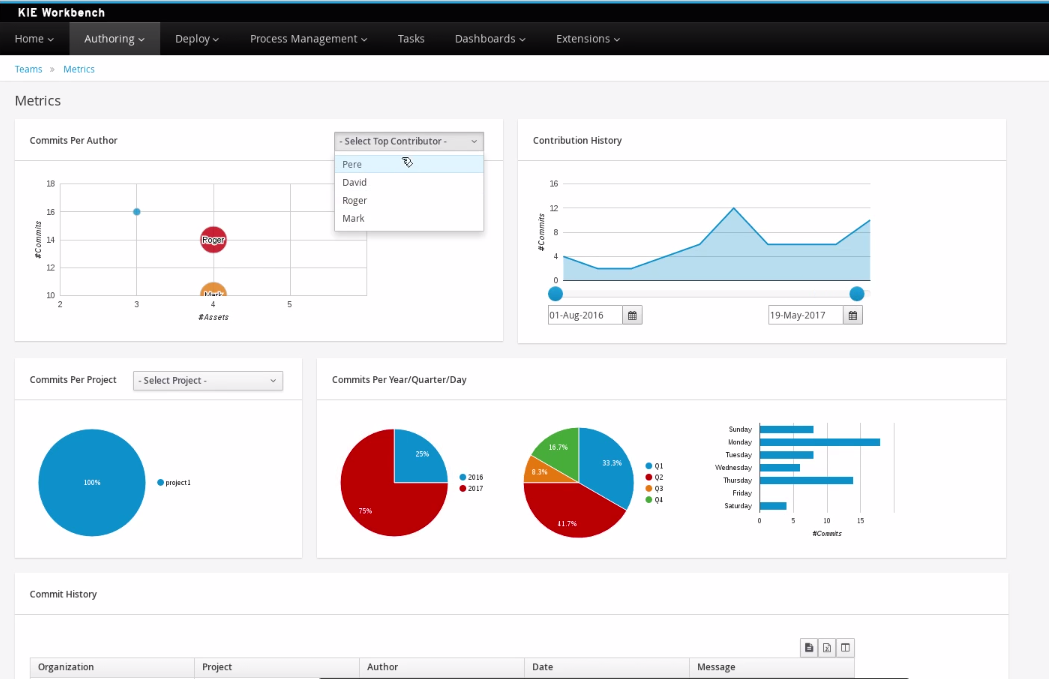
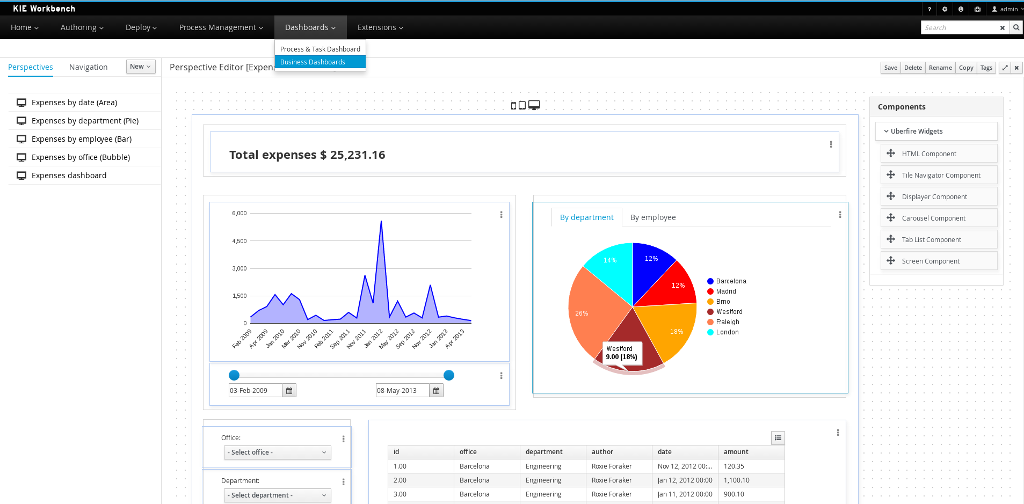
Business dashboards
Where it was possible to create your own dashboards in v6 using the (separate) dashbuilder application, dashbuilder has been refactored completely to better align with the workbench technology. It is now possible to do all of this from within the workbench, and integrate it in your own applications as well.
Process and task admin api
A new API has been introduced that includes powerful capabilities for process and task administrators. The process admin API allows you to:
- get all process definition nodes
- cancel node instance
- retrigger node instance
- update timer (absolute or relative)
- list timer instances
- trigger node
The task admin API allows you to:
- add/remove potential owners, excluded owners and business admins
- add/remove task inputs and outputs
- list/create/cancel escalations and notifications
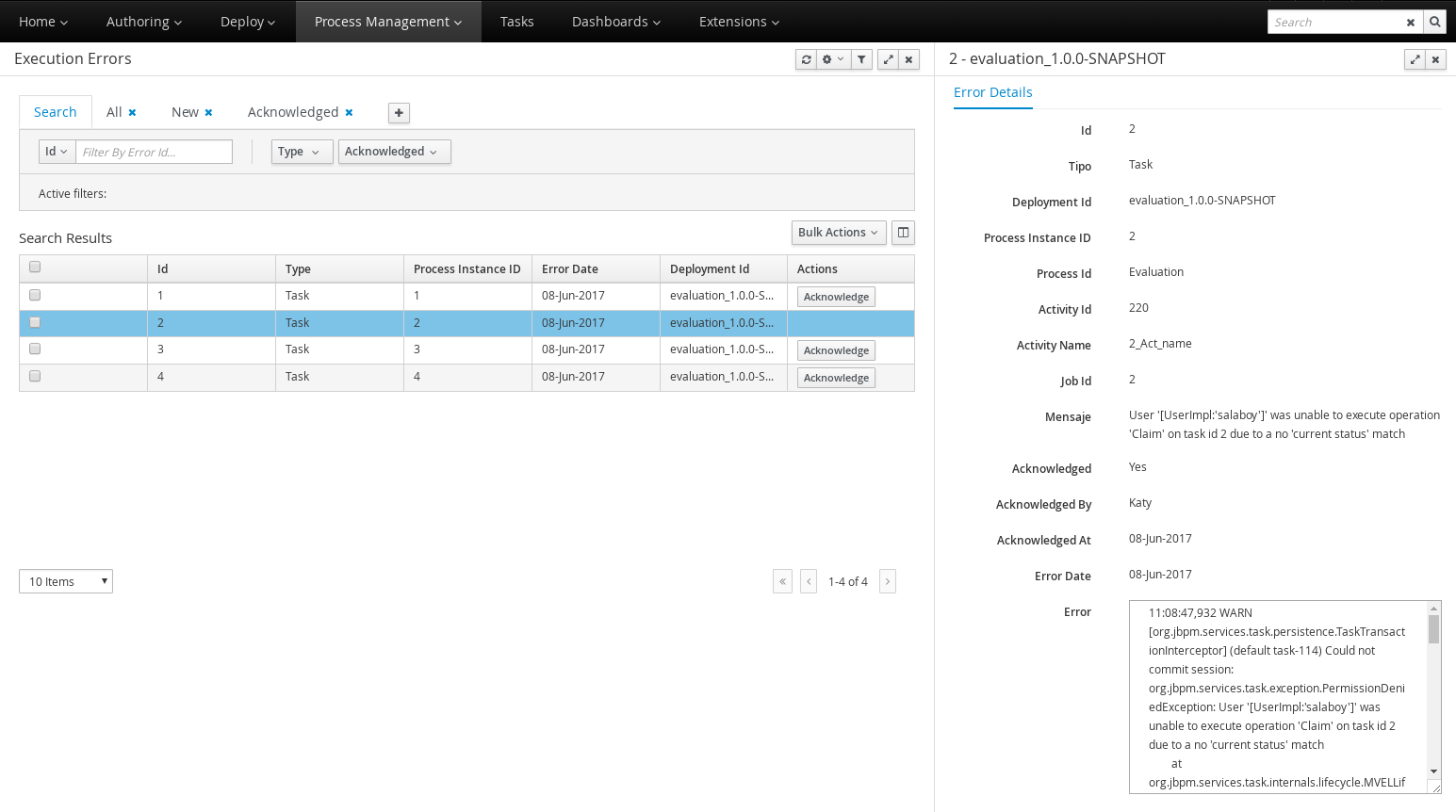
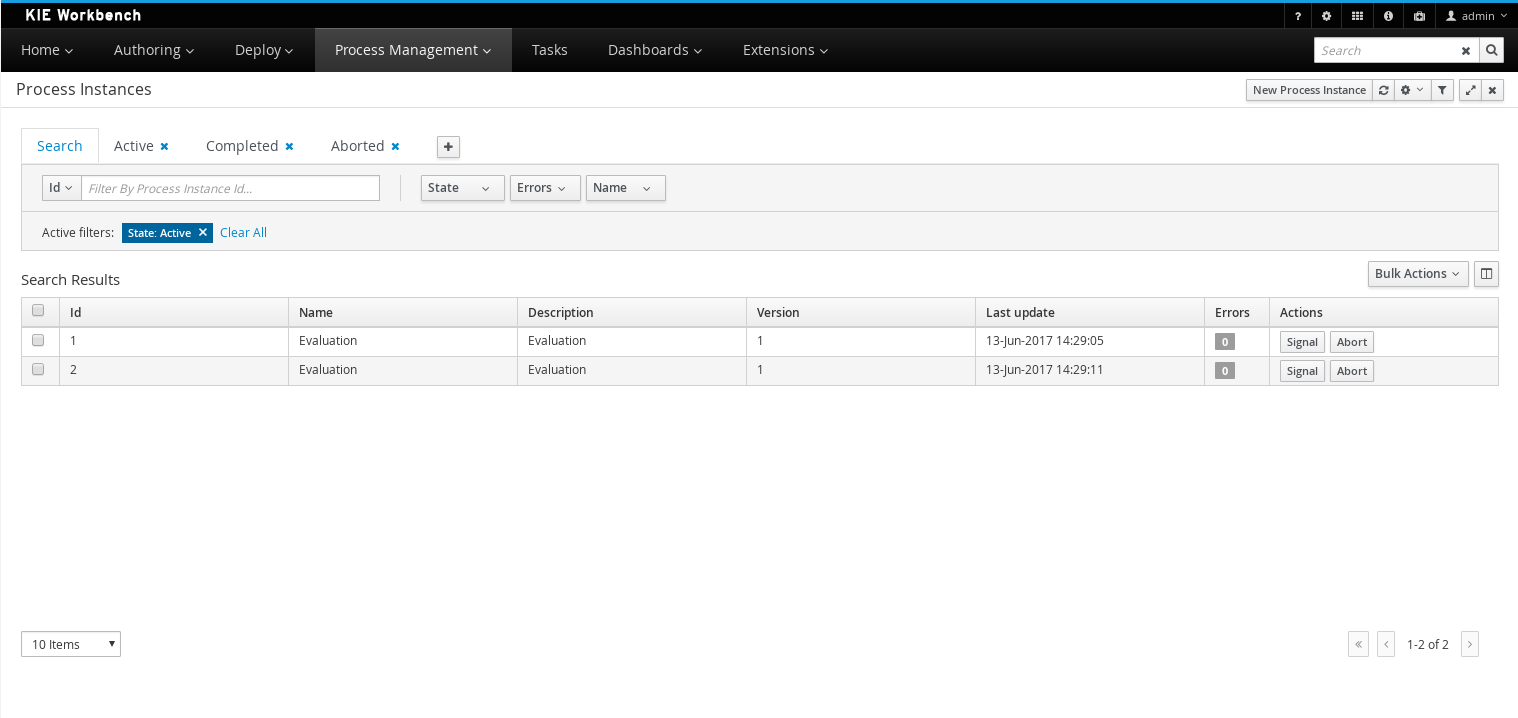
Process and task console separate from execution server
Our web-based management and monitoring console used an embedded execution server in v6 to execute all process and task operations. We also offered a standalone process execution server. In v7 the monitoring console is a UI front-end only, all requests for process and task data and operations on them are delegated to a standalone execution server. The main advantage is that the console can now 'connect' to basically any (set of) execution servers out there.
When multiple independent kie-servers are used, you can either connect
to a specific one or use the smart router to aggregate information
across multiple servers:
-
requests can be sent to the smart router, it will be able to figure
out which of the known kie-server instances the request should be sent
to
-
when trying to retrieve information, the smart router can collect
information from different servers and aggregate that information for
you
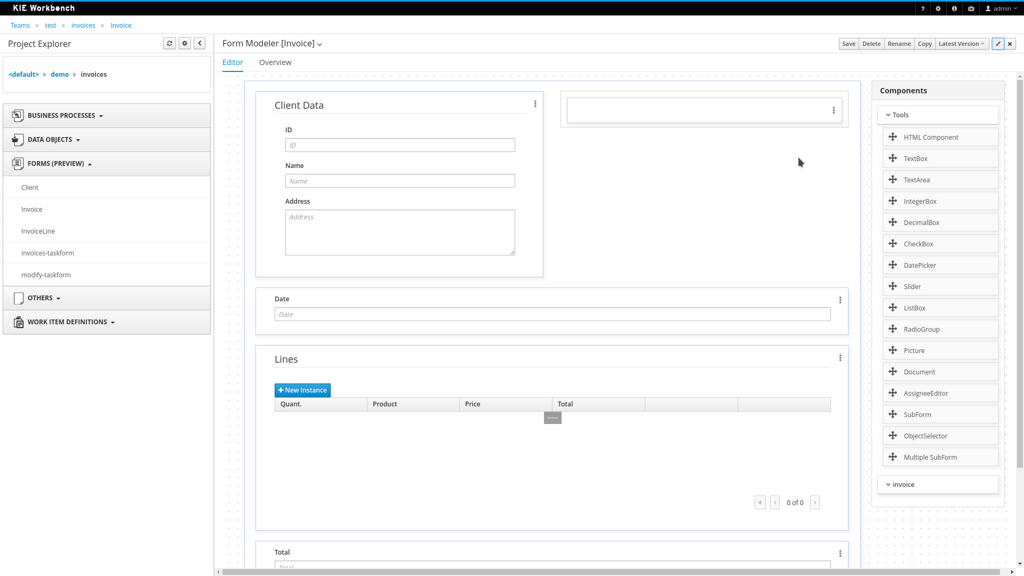
Preview of new form modeler
The form modeler has been upgraded significantly as well. The new form layout system (based on the Bootstrap Grid system) allows more advanced and flexible layouts, new widgets, generation of forms, a Java-based file format and much more. We will do a few more feature enhancements before we will remove the old form modeler in one of the future minor releases.
Preview of a new process designer
We are working on a completely new web-based process designer, and this release introduces a early preview (where we only support a small subset of the full feature set). The idea is to move away from a very developer-focused UI and introduce an easier to use interface for different kinds of users. Properties behave much more as advanced forms (rather than a table of key-value pairs) and the user is assisted as much as possible whenever we can (using content assist, etc.).
Currently it is still recommended to use the existing designer for modeling your business processes (since the capabilities of the new one are still limited) but feel free to give it a try and let us know what you think.
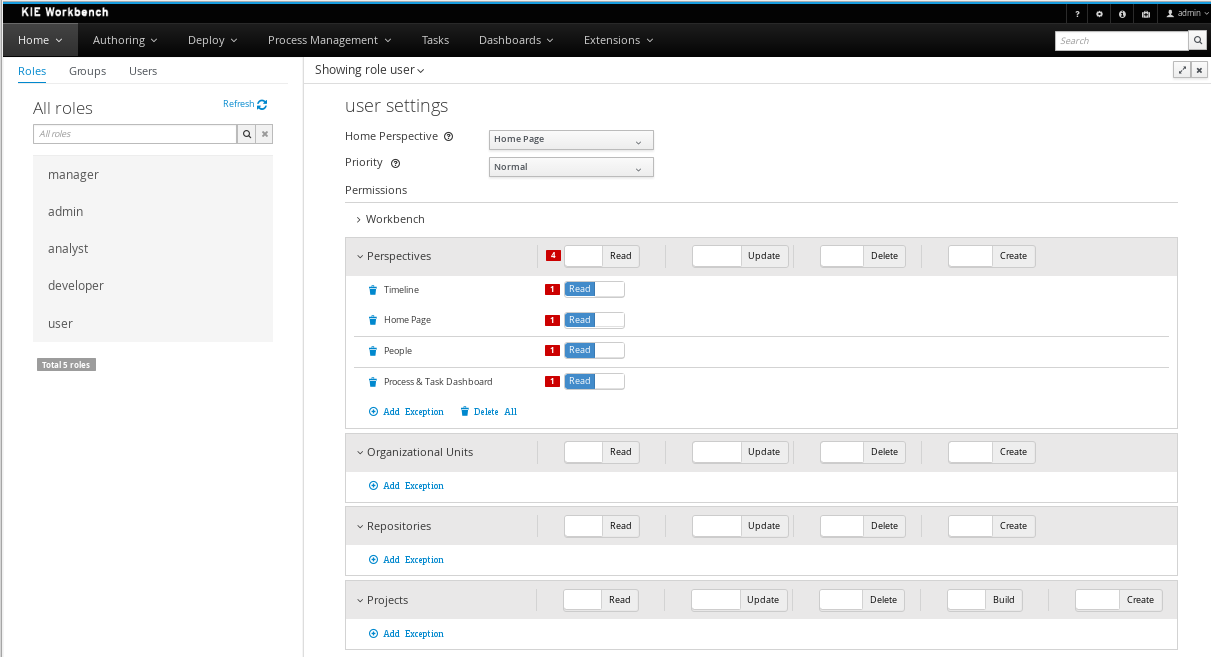
A new security management UI
While it was already possible to define users and groups (and their relationship), a new security management UI allows you to define permissions for all of these users (or groups). You can control who can use which part of the UI, but also which projects users have access to, etc.
Decision Model and Notation (DMN)
Drools has introduced support for the DMN standard, and since jBPM integrates closely with Drools for rule execution, you can now trigger DMN rules from a business rule task.
Other features
- Minimum Java version was upgraded to Java8
- Support for WildFly 10 and EAP7
- New preferences page
- Data source management
Please take a look at the full
release notes for more details. jBPM is integrated closely with the Drools and Optaplanner projects (for business rules and constraint optimization respectively), so take a look at the Drools and Optaplanner release announcements for more details on how some of the new features you can use in combination with your processes as well !